- Economics is the study of how human make decisions in the face of scarcity. Scarcity means that wants exceed available resources.
General Quantities
- Marginal analysis is just a discretized form of the derivative.
-
Example: The marginal cost with respect to quantity is
-
Notation: For convenience, when we say, the marginal
with respect to , we mean By default, assume
is quantity We may also write this as a derivative as
.
-
The Market
- The division of labor means that the way one produces a good or service is divided into a number of tasks that different workers perform rather than one person doing al the tasks.
- Division of labor counters scarcity.
- Division of labor increases production for three reasons 1
- Specialization of workers on tasks they are well suited for, which makes them more effective.
- Specialization leads to a feedback loop where workers learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This also leads to innovation.
- Specialization takes advantage of economies of scale where as production increases, the average cost of production for each individual unit decreases.
- This necessitates trade because each individual specializes and must exchange their services for other needs that they are unable to produce.
- Economies are systems.
- Economics teaches you how to think, not what to think 2
- A simple economic model is the Circular Flow Model
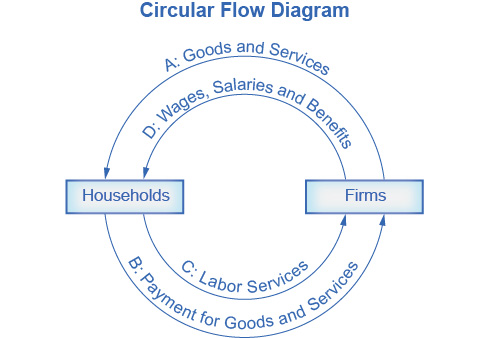
- Economies can be organized into different ways.
- Traditional - what you produce is what you consume. It is driven by tradition and there is little economic progress or development
- Command - economic effort is devoted to goals passed down from the government, which dictates what gets produced and what gets consumed.
- Markets - decision making is decentralized and is based on markets — institutions that bring buyers and sellers together.
- Private enterprises own and operate production based on supply and demand.
- Income is based on the ability to convert resources into something socially beneficial.
- Market-oriented economies have fewer regulations, often just enough to facilitate fair trade.
- Markets allocate goods to the people who value them the most, under the assumption that the value of the good is easily understood by all market participants.
- Underground / Black Market - often present in heavily regulated economies. This market is unregulated.
Unfiled
- Tax Incidence - the analysis of how tax burdens can be divided between consumers and producers
Topics
- Microeconomics - focuses on the actions of individual agents within the economy
- Macroeconomics - focuses on the economy as a whole.
- Money
- Computational Economics