- Intent: Ensure a class only has one instance, and provide a global point of access to it
Structure §
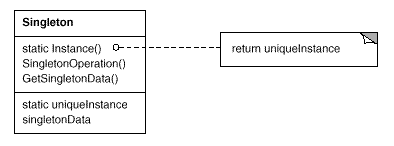
Image from: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vissides
Applicability §
- There must be exactly one instance of a class accessible to clients from a well-known access point.
- When the sole instance should be extensible by subclassing and clients should be able to use an extended instance without modifying their code.
Consequences §
- Controlled access to sole instance.
- Reduced name space
- Permits refinement of operations and representation.
- Permits a variable number of instances.
- More flexible than class operations (i.e. static member functions)
Implementation §
- Ensure a unique instance by hiding its constructor.
Subclassing §
- Determine which singleton to use in a singleton’s instance operation.
- Take the implementation of Instance out of the parent class
- Use a registry of singletons.
