- Intent: Given a language, define a representation for its grammar along with an interpreter that uses the representation to interpret sentences in the language.
Structure §
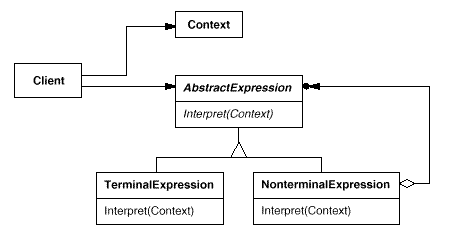
Image from: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vissides
Applicability §
- When there is a language to interpret and they can be represented as Abstract Syntax Trees
- The grammar is simple
- Efficiency is not a critical concern.
Consequences §
- It’s easy to change and extend the grammar
- Implementing the grammar is easy
- Complex grammars are hard to maintain
- Adding new ways to interpret expressions
Implementation §
- Creating the Abstract Syntax tree is not defined by the interpreter pattern
- Use Visitor pattern if it’s common to create a new interpreter.
- Share terminal symbols in the grammar via the Flyweight pattern.
