- Intent: Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem and make it easier to use.
Structure §
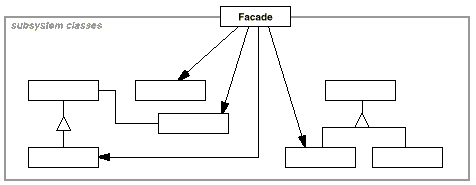
Image from: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vissides
Applicability §
- You want to provide a simple interface to a complex subsystem
- There are many dependencies between clients and the implementation classes of an abstraction promoting subsystem portability
- You want to layer subsystems.
Consequences §
- It shields clients from subsystem components, reducing the objects the clients deal with and making the subsystems easier to use.
- It promotes weak coupling between subsystems and their clients—allowing varying the components of the subsystem independent of the client.
- Removes circular or complex dependencies.
- It doesn’t prevent applications from using subsystems if they need to.
Implementation §
Reducing client-subsystem coupling: §
- Make façade an abstract class with concrete subclasses, allowing variation in implementation.
- Configure the façade with different subsystems.
Subsystem Classes §
- Public vs private subsystem classes. It is recommended to make them private to follow the encapsulation.
