- Aka: Handle / Body
- Intent: Decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently
Structure §
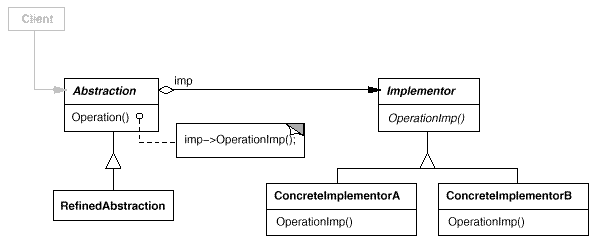
Image from: Gamma, Helm, Johnson, and Vissides
Applicability §
- You want to avoid a permanent binding between an abstraction and its implementation. This might be the case when implementation must be selected or switched at runtime.
- Both abstractions and implementations should be extensible by subclassing.
- Changes in the implementation of an abstraction should have no impact on clients.
- You have a proliferation of classes
- You want to share an implementation using multiple objects and this fact should be hidden from the client
Consequences §
- Implementation is not bound permanently to an interface.
- Encourages a better structured system via layering.
- Improved extensibility for abstraction and implementation.
- Hiding implementation details from clients.
- Complicates dependency injection
- Builder classes are forced to be mutable
Implementation §
- If there is only one implementor, then creating an abstract implementor class isn’t necessary.
- Creating the right Implementor object:
- If Abstraction knows all Concrete Implementors, then it can instantiate one of each in its constructor and decide.
- Choose a default implementation to change later.
- Delegate the decision to another object.
- Abstractions can share implementors.
- Use multiple inheritance
